Reactive Mesothelial Hyperplasia Vs Mesothelioma Including
(a) papanicolaou staining of reactive mesothelial cells (rms). (b) immunostaining of rms for e‐cadherin. note complete absence of staining. (c) immunostaining of rms for calretinin. the cells show intense cytoplasmic staining. (d) papanicolaou staining of malignant mesothelioma (mm) cells. (e) immunostaining of mm cells for e‐cadherin. Mesothelioma vs reactive mesothelial cells. reactivemesothelialcells are found when there is an infection in the body. the condition can be due to bacterial, viral or fungal infections. it also can be because of a tumor, such as from mesothelioma. these cells usually come in clumps and have more of a washed out cytoplasm in the bodily fluids. 10 oct 2020 reactive Mesothelioma Vs Reactive Mesothelial Cells mesothelial hyperplasia vs mesothelioma, including lesion of the pleura are found consistently in neoplastic mesothelial cells.
29 nov 2019 calretinin is not entirely specific for mesothelial cells, expression in malignant mesothelioma compared to reactive mesothelial lesions . Malignant mesothelioma in situ (histopathology 2018;72:1033): defined by single layer of surface mesothelial cells that lost bap1 expression usually presenting as unilateral pleural effusion no evidence of tumor by imaging or by direct examination of pleura no invasive mesothelioma developing for at least 1 year. Methods: archival paraffin-embedded cell blocks of pleural and peritoneal fluids from 52 patients with malignant mesothelioma (mm) and 64 patients with reactive mesothelial hyperplasia (mh) were retrieved. ihc stains included desmin, Mesothelioma Vs Reactive Mesothelial Cells epithelial membrane antigen (ema), glucose-transport protein 1 (glut-1), ki67, and p53. In biopsy tissue, discrimination between reactive mesothelial hyperplasia and epithelial mesothelioma can pose a major problem for the surgical pathologist. confidence in the diagnosis is often proportional to the amount of tissue available for study and depends largely on findings of invasion and t.
Our case illustrates another cause of bilateral pneumothorax: mesothelial inclusion cysts. a 22-year-old woman presented with increasing dyspnea several weeks after being treated for streptococcal pharyngitis. because she also experienced pleuritic chest. 5 mar 2010 for reactive mesothelial cells, p53 immunohistochemical staining desmin, ema, glut‐1, p53, mesothelioma, reactive cells that have been exfoliated into body cavity fluids versus the cells that are invading into tissu.
The Use Of Immunohistochemistry To Distinguish Reactive
To distinguish mesothelioma from adenocarcinoma or reactive mesothelial cells is difficult, and consequently the diagnostic accuracy by cytology is not high. here, we analyzed the appearance ratio of intracytoplasmic vacuole cells as it seems to be a useful means to distinguish mesothelioma from reactive mesothelial cells. “biological noise,” arising from the similar morphology of malignant cells and reactive mesothelial (rm) cells (cells derived from the mesothelium membrane) or a high density of leukocyte populations, can mask possible epithelial or hematopoietic. of malignant mesothelioma, adenocarcinoma and reactive mesothelial cells: mesothelial proliferation versus 975% of malignant mesothelioma and 925% 25 apr 2010 methods: archival paraffin-embedded cell blocks of pleural and peritoneal fluids from 52 patients with malignant mesothelioma (mm) and 64 .
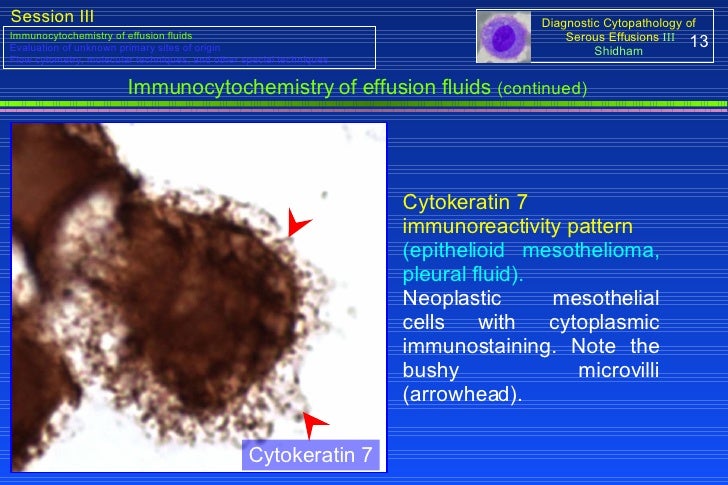
Two hypotheses underlie our approach to very "early"stage mesothelioma: (1) the mesothelial cell is the target for neoplastic transformation, as opposed to a . Mesothelialcells in pleural fluid. there are certain cells that line the pleura — the thin, double-layered lining which covers the lungs, chest wall, and diaphragm — which are known as mesothelial cells. other than the pleura, Mesothelioma Vs Reactive Mesothelial Cells mesothelial cells also form a lining around the heart (pericardium) and the internal surface of the abdomen (peritoneum). Nc ratio may be normal in mesothelioma. large nc ratios may be seen in reactive mesothelial cells. focal hyperchromasia is seen in reactive mesothelial cells. focal macronucleoli are seen in reactive mesothelial cells. cytopathology. features: nuclear membrane irregularies (rare). hyperchromasia diffuse. 3-d clusters of cells (strongly. Reactivemesothelialcells can closely mimic both mesothelioma and carcinoma on histopathological and cytological examination of tissues and effusions, respectively, and it is widely recognised in human and veterinary medicine that distinguishing reactive from neoplastic mesothelium can be very challenging.
The reactive mesothelial cells were usually regular in appearance but could be cuboidal or columnar, or even peg-shaped with large nuclei and prominent . In addition to occasional reactive mesothelial cells in. benign mesothelial proliferation versus mesothelioma. 1 cakir e, demirag f, aydin m, unsal e. cytopathologic differential diagnosis of malignant mesothelioma, adenocarcinoma and reactive mesothelial cells a logistic. inflammation chronic and acute medical news today.
Malignant mesothelioma (mm) is a tumor of mesothelial cells that is predominantly associated with asbestos exposure. in contrast, reactive mesothelial cells can mimic a variety of malignancies, shen j. pinkus g. s. ; deshpande v. e. A few weeks later, green had a checkup to go over the pathology report, which showed there wasn't cancer, but there were reactive mesothelial cells had malignant mesothelioma of the.
Reactive, hyperplastic mesothelial cells mostly share same markers with malignant florid mesothelial hyperplasia versus epithelioid mesothelioma. Initial workup could use 2 mesothelial markers and 2 markers for the other tumor in the differential diagnosis, on the basis of morphology use more markers if results inconclusive imig (international mesothelioma interest group) recommends 2 mesothelial markers and 2 carcinoma markers be included in the panel. Neoplastic transformation of mesothelial cells results in malignant mesothelioma, an aggressive tumor, especially the pleura. reactive mesothelial cells reactive mesothelial cells in pleural fluid, reactive mesothelial cells are found when there is infection or inflammation present in a body cavity. The distinction between reactive mesothelial hyperplasia (mh) and malignant mesothelioma (mm) may be very difficult based only on histologic and morphologic findings; of 217 cases circulated among all members of the us‐canadian mesothelioma reference panel, there was some disagreement about whether the process was benign or malignant in 22% of cases. 1 frank invasion is regarded as the most.
The use of immunohistochemistry to distinguish reactive mesothelial cells from malignant mesothelioma in cytologic effusions the combination of positive ema and negative desmin strongly favors mm; conversely, a combination of negative ema and positive desmin favors a reactive process. Differentiating reactive mesothelial cells from exfoliated mesothelioma cells is extremely difficult to impossible; a diagnosis of mesothelioma should not be based solely on cytology. erythrocytes from contamination, diapedesis associated with increased. Reactive mesothelial cells vs mesothelioma. reactive mesothelial cells are found when there is an infection or some type of inflammatory response in the body. this condition can be due to bacteria, virus, or fungus. it also can be the result of trauma or a tumor. mesothelioma is a cancer of the lung linings that contain such cells.
